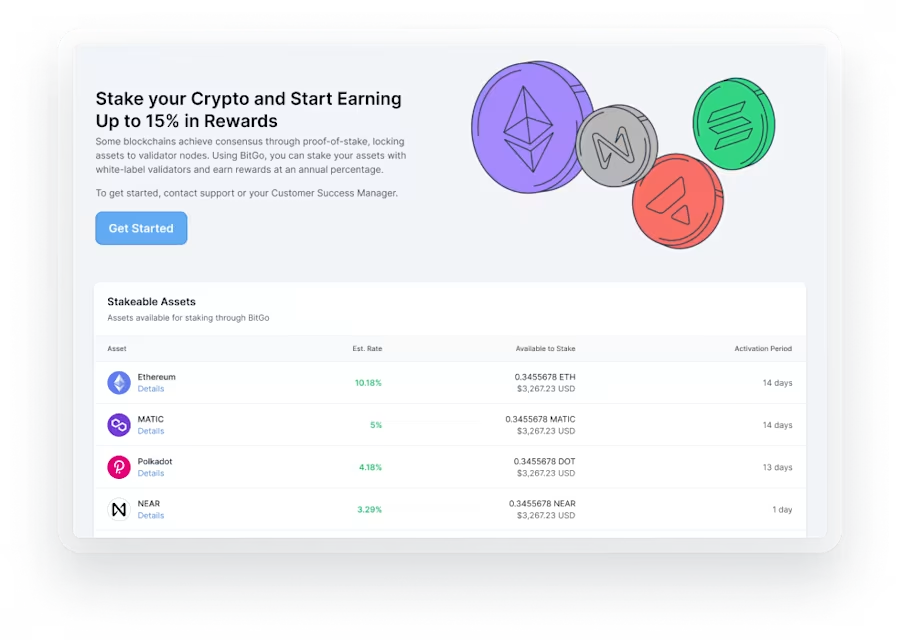
Knowledge Staking as a Service
Staking as a Service involves outsourcing the staking method to a specialized service service, often referred to as a staking company or platform. In place of controlling the complexities of running a staking node, sustaining budget security, and ensuring network uptime, investors can delegate these responsibilities to the service provider. In exchange, they receive staking returns and different advantages without the need for technical expertise or constant monitoring.
Benefits of Staking as a Service
1. Use of Passive Income:
Among the principal advantages of Staking as a Service is the ability to make inactive revenue from staking rewards. By delegating their tokens to a staking provider, investors can be involved in the staking method without actively controlling a staking node or maintaining budget security. That passive income stream can supplement standard investment strategies and give a steady get back on investment.
2. Reduction of Technical Complexity:
Working a staking node requires technical familiarity with blockchain practices, budget management, and network security. Staking as a Service simplifies this method by outsourcing all technical elements to skilled service providers. Investors take advantage of the provider's knowledge in sustaining nodes, ensuring uptime, and managing process improvements, letting them concentrate on investment strategy as opposed to specialized operations.
3. Diversification and Chance Management:
Staking as a Service helps investors to diversify their cryptocurrency holdings across multiple staking tools and protocols. Rather than concentrating assets on a simple blockchain network, investors may spend their tokens to various staking providers, spreading risk and possibly raising rewards. That diversification strategy improves portfolio resilience and mitigates the impact of market variations on attached assets.
4. Variable Staking Options:
Staking as a Service offers flexibility with regards to staking options and token liquidity. Investors can choose from various staking periods, prize structures, and withdrawal options depending on the expense goals and risk tolerance. Some companies present quick liquidity alternatives, enabling investors to withdraw secured tokens or rewards without extended lock-up times, increasing liquidity management.
5. Enhanced Protection and Reliability:
Respected Staking as a Service vendors prioritize security measures to safeguard investors' assets and guarantee the consistency of staking operations. These vendors utilize strong protection protocols, such as cold storage wallets, multi-factor validation, and regular safety audits, to safeguard secured tokens against unauthorized accessibility and potential internet threats. Investors take advantage of enhanced security without compromising on staking rewards.
6. Involvement in Governance:
Several Staking as a Service systems offer investors the ability to take part in blockchain network governance. Token cases may election on process improvements, governance proposals, and ecosystem developments, influencing the long run path of the network. That active participation empowers investors to subscribe to decentralized governance and align their interests with the long-term success of the blockchain platform.
Criteria for Investors
1. Service Company Status and Monitor Report:
Before choosing a Staking as a Service provider, investors must perform thorough due persistence on the provider's name, background, and security practices. Evaluations, testimonials, and community feedback can offer useful insights to the stability and trustworthiness of the service provider.
2. Charge Structures and Transparency:
It's important to understand the charge structures related to Staking as a Service , including administration expenses, efficiency fees, and withdrawal fees. Translucent payment disclosure ensures investors can effectively gauge the cost-effectiveness of the service and make educated choices about staking participation.
3. Regulatory Conformity and Appropriate Concerns:
Cryptocurrency regulations vary across jurisdictions, and investors should make certain that Staking as a Service complies with relevant regulatory requirements. Knowledge legal considerations, duty implications, and submission obligations may mitigate regulatory dangers and ensure legitimate submission when participating in staking activities.
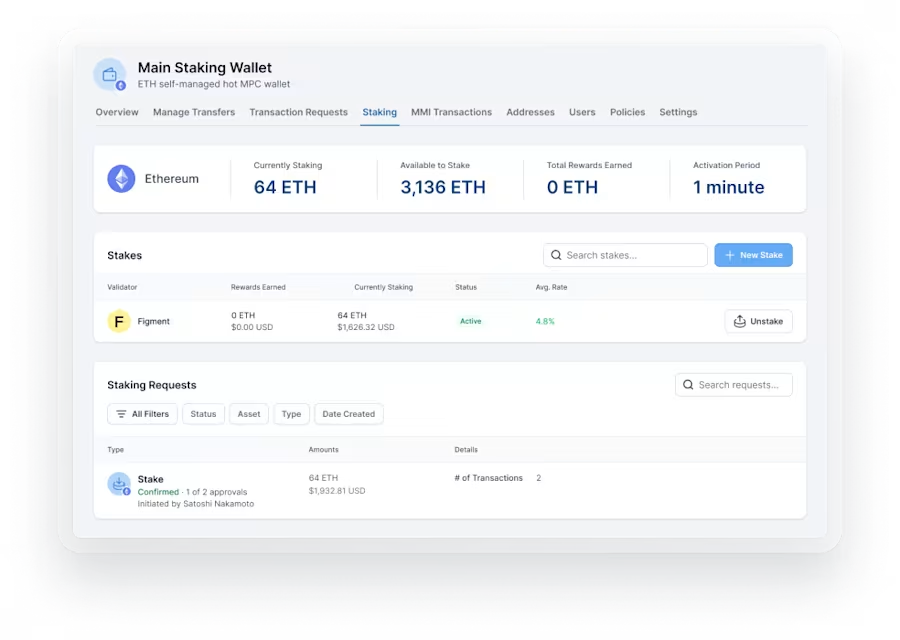
Conclusion
Staking as a Service presents convincing advantages for cryptocurrency investors seeking to generate passive income, be involved in blockchain networks, and diversify their expense portfolios. By outsourcing the specialized complexities of staking to skilled service companies, investors may appreciate increased safety, mobility, and involvement in blockchain governance. However, it's critical for investors to conduct thorough study, examine chance facets, and choose respected service vendors to increase the benefits of Staking as a Service effectively.
No comments:
Post a Comment